What Are Antioxidants
Everyone’s talking about antioxidants—their health benefits, foods that are good sources of them, and different kinds—but what are they, anyway?
Antioxidants work to help defend your cells against tiny molecules called free radicals, which can cause oxidative stress throughout the body. Sometimes called “free radical scavengers,” antioxidants help protect against cell damage caused by these marauding molecules.
Antioxidants protect you from free radicals and oxidative stress
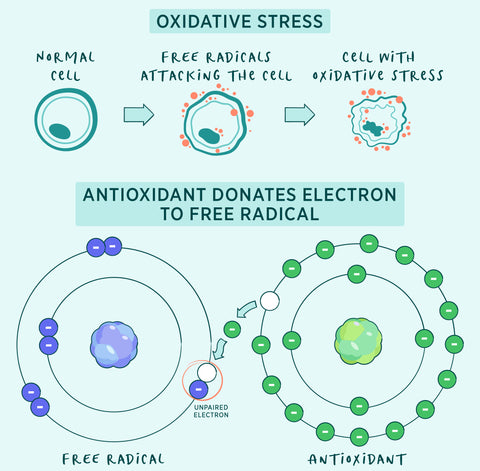
The way antioxidants defend your cells from free radicals is fascinating! But we have to take it back to high school chemistry to explain. Every molecule has a certain number of electrons. Most of the time, molecules have an even number of electrons that come in pairs, making them relatively stable compared to their odd-numbered counterparts.
Free radicals have an odd number of electrons with missing pairs, and it’s that unpaired electron that makes them “unstable”. In an effort to stabilize, they bounce around your body looking for a pair, stealing electrons from other molecules, and potentially damaging those molecules in the process.
Antioxidants also have an odd number of electrons, but they don’t go around stealing them from other molecules in the name of stability. Instead, antioxidants give up electrons to free radicals so they can both have an even number of electrons; bringing both molecules to a neutral state and leaving your healthy cells intact!
That said, having free radicals in your body is natural! They’re byproducts of healthy aging, daily bodily processes like digesting food, and even working out. It’s just that the amount of free radicals in your body can become imbalanced when you're exposed to environmental pollutants, toxins, and even too much sunlight. When free radicals predominate, it often leads to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress happens when the number of free radicals exceeds the number of antioxidants. This imbalance can affect your whole body, influencing your energy, brain health, and skin and hair quality.
Aging Benefits of Antioxidants
On the flip side, a diet rich in antioxidants can help promote healthy aging, and even though there’s a lot of buzz around their skin benefits, antioxidants can promote vitality all throughout your body–from your skin, hair, and nails, to your organs, blood vessels, and everything else.
Many people prioritize getting enough antioxidants because they promote well-being in so many different parts of your body. Studies show they foster optimal immune health, brain function, mood, a healthy gut, and so much more—all while supporting healthy skin and collagen production so you can look as good as you feel!
Dietary Sources of Antioxidants
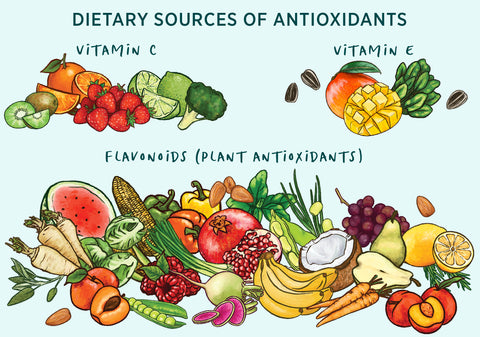
You can harness the healthy-aging benefits of antioxidants by being intentional about the things you eat. There are thousands of different antioxidants in fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and other natural food sources. Some of the most common antioxidants in your food are vitamin C, vitamin E, and flavonoids.
Vitamin C
Did you know that vitamin C is an antioxidant? It’s well known for promoting a healthy immune system, but that’s not all it’s good for. Vitamin C’s antioxidant properties also support optimal cellular function and a healthy heart, all while leaving you with a healthy, natural glow!
You can get more vitamin C in your diet by eating citrus fruit, tomatoes, kiwi, strawberries, broccoli, and more. Looking for an even easier way? Try out Pure Radiance C. Each serving has 130% of your recommended daily value of vitamin C and is made exclusively from vitamin C-rich fruits and berries.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E might be vitamin C’s less popular cousin, but its health benefits are just as awe-inspiring. It travels around your body nourishing the health of your eyes, brain, and other tissues. As a result, it helps promote healthy vision and cognition.
Increase the amount of vitamin E you consume by seeking out food sources. Sunflower seeds, peanut butter, mango, and spinach are rich in vitamin E. You can also look for a supplement that matches your health goals.
Flavonoids (plant antioxidants)
If your mom ever told you to eat the rainbow or a colorful plate, she was onto something. It turns out the bright colors in vegetables come from a class of antioxidants called flavonoids, which promote heart and brain health.
There are all sorts of fruits, vegetables, and herbs you can eat or drink to increase the amount of flavonoids in your diet. Choosing colorful fruits and veggies at each meal is a great way to prioritize getting plenty of flavonoids each day.
If piling your plate with plants every day is easier said than done, consider adding a high-quality supplement to your routine to fill in the gaps. You can find plenty of antioxidants in our flavonoid-rich Organic Berry Power, made with 20 of the most nutrient-dense berries and fruits we could find from around the world. It’s an easy, delicious way to nourish and defend your mind and body!


